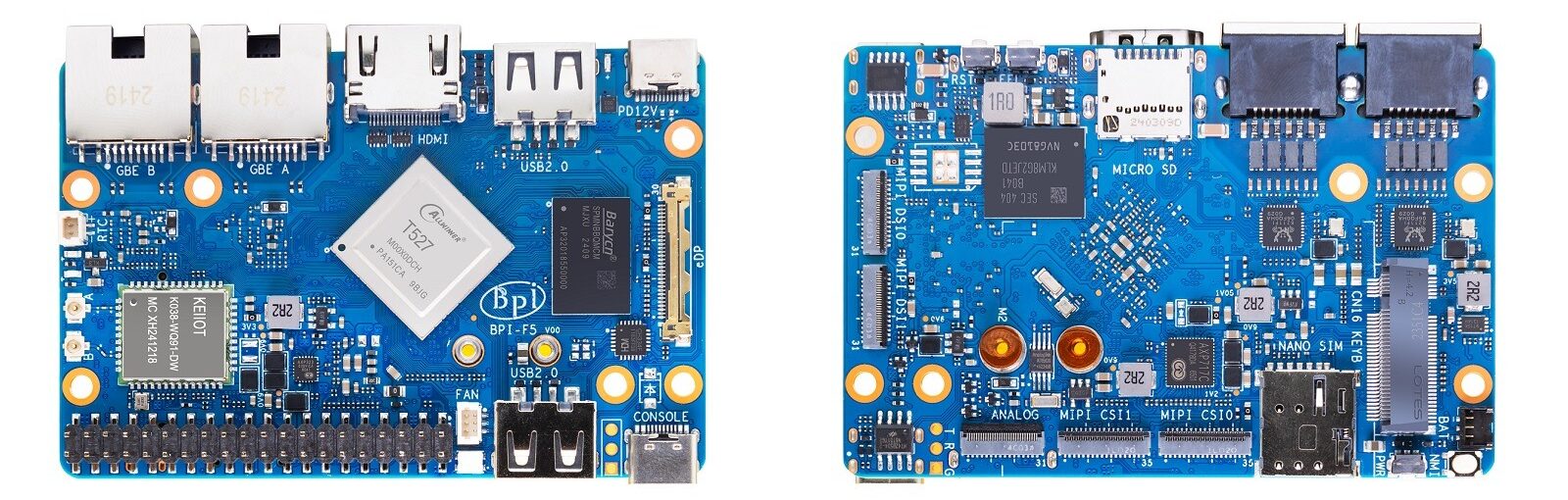
Banana Pi BPI-F5 is a new product in the single-board computer (SBC) market featuring a small form factor and powerful hardware solutions. The board is an Allwinner T527 based platform designed to provide a balance of performance and efficiency, capable of performing simple general computing tasks to AI-driven applications. Its industrial-grade and credit-card-sized design gives it a wide range of applications among makers and engineers alike.
The board focuses on a broad spectrum of applications, such as industrial control, automotive systems, robotics, and edge computing. The BPI-F5 operates between -40°C to 80°C with a wide operating temperature span, which is its advantage over other models because it can be used even in harsh environments.
Previously, we covered the Banana Pi BPI-F4, an open-source industrial control board based on the Sunplus SP7350 SoC. You can check it out if you’re interested in exploring that board.
Banana Pi BPI-F5 SBC Specifications:
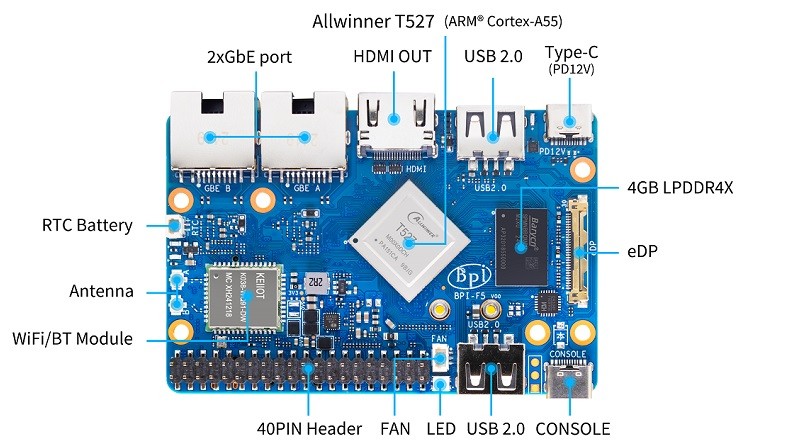
Banana Pi BPI-F5 uses Allwinner T527 SoC (DynamIQ big.LITTLE) which is an octa-core ARM Cortex-A55 processor with a frequency of 1.8 GHz. It is powered by the ARM G57 MC1 graphical processor, which supports OpenGL ES 3.2 and Vulkan 1.1-1.3, plus OpenCL 2.2. The board also integrates a 2 TOPS NPU with a 512 KB buffer for AI inference, a HiFi4 DSP running at 600 MHz for multimedia processing, and an independent RISC-V MCU up to 200 MHz for real-time control under RTOS.
The system includes 2 GB or 4 GB LPDDR4x memory (default 4 GB) and eMMC storage options of 8 GB or 32 GB (default 32 GB), along with a microSD slot for expansion. Connectivity options cover dual Gigabit Ethernet, Wi-Fi 6, and Bluetooth 5.3. For display and multimedia, the BPI-F5 supports HDMI 2.0b output up to 4K @ 60 fps, an eDP connector, and a 4-lane MIPI-DSI interface, with audio available through HDMI and a headphone jack. Camera support comes via dual MIPI-CSI connectors.
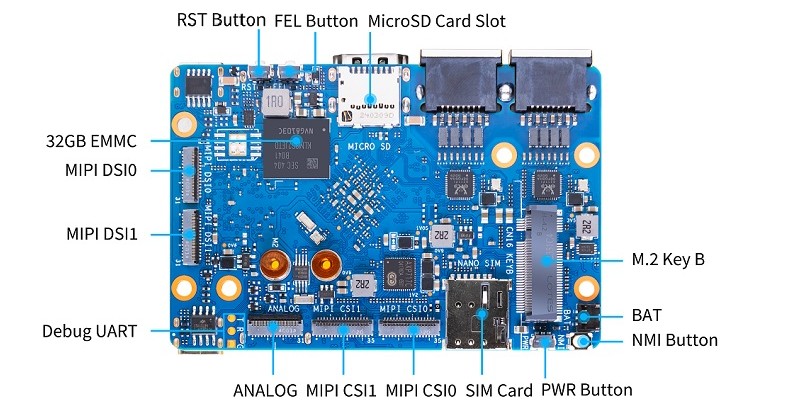
Expansion and I/O interfaces consist of 40-pin GPIO, M.2 Key B slot, SIM, UART debug, and various USB options, two USB 2.0 hosts, USB Type-C 3.0 host, and USB Type-C ports with PD. Other features are reset, FEL, NMI, and power buttons, RTC battery connector, fan connector and LED indicators. The board is 92 x 62 x 14.6 mm in size with a weight of approximately 42 g to ensure an extended operating temperature of -40°C to 80°C, and as such can be used in industry and embedded applications.
Banana Pi officially documents Armbian on BPI-F5, including early firmware and driver content in the documentation. The board is compatible with a wide variety of projects by allowing developers to configure their custom Linux-based environment on the board. The wider software support will develop as things progress, making it more stable and compatible in the long run.
The Banana Pi BPI-F5 is not yet available for purchase, and pricing has not been announced. However, its Wiki page already provides early documentation and specifications for developers.
Images used courtesy of Banana Pi.


Can I use it in my line following robot project??
Yes, but with caveats. The BPI-F5 is powerful enough to run the line-following brain (especially if you want camera-based or ML/vision line detection using its NPU), but it’s not ideal as the sole real-time motor controller. Use it for perception, planning and higher-level control, and pair it with a small microcontroller (ESP32/STM32/Arduino) or dedicated motor driver for low-latency PWM/encoder handling.